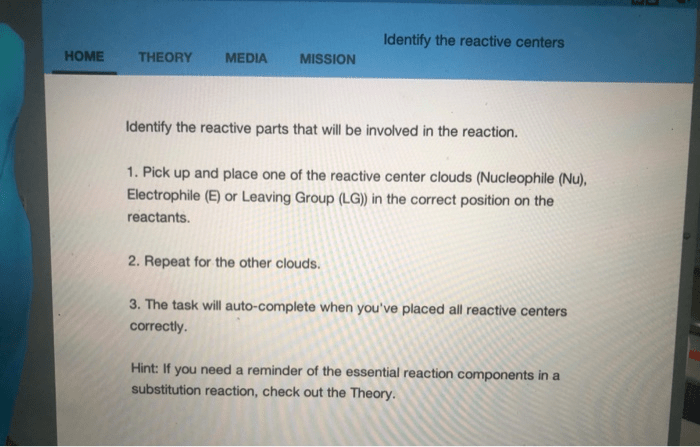
Identify the reactive centers by placing the reactive center clouds, a fundamental concept in chemistry, provides a systematic approach to understanding and predicting chemical reactions. Reactive center clouds, electron-rich regions within molecules, play a pivotal role in determining the reactivity and selectivity of chemical transformations.
This article explores the theoretical foundations, identification methods, and practical applications of reactive center cloud theory, offering valuable insights into the behavior of molecules and the design of new materials.
Reactive Center Cloud Theory
The reactive center cloud theory is a conceptual framework that describes the distribution of electrons in a molecule. It proposes that the electrons in a molecule are not evenly distributed but rather concentrated in certain regions called reactive center clouds.
These clouds are believed to be the sites of chemical reactions, where the electrons are most likely to interact with other molecules and undergo chemical transformations.
The reactive center cloud theory has significant implications in understanding chemical reactions. By identifying the reactive center clouds in a molecule, chemists can predict the most likely reaction pathways and the products that will be formed. This knowledge can be used to design new molecules with specific properties and to control the outcome of chemical reactions.
Significance of Reactive Center Clouds in Chemical Reactions
- Reactive center clouds are the sites of chemical reactions.
- They determine the most likely reaction pathways.
- They can be used to predict the products of a reaction.
Examples of Reactive Center Clouds in Different Types of Reactions
- In nucleophilic reactions, the reactive center cloud is located on the nucleophile.
- In electrophilic reactions, the reactive center cloud is located on the electrophile.
- In free radical reactions, the reactive center cloud is located on the free radical.
Identification of Reactive Centers
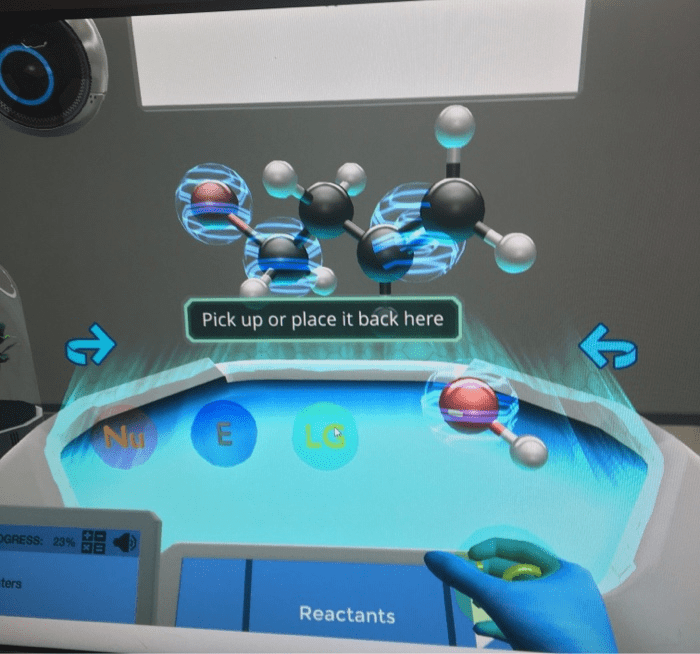
There are a number of methods that can be used to identify reactive centers in a molecule. One common method is to use molecular modeling software. This software can calculate the electron density of a molecule, which can then be used to identify the regions where the electrons are most concentrated.
Another method is to use computational chemistry. This approach can be used to calculate the energy of a molecule as it undergoes a reaction. By identifying the transition state of the reaction, it is possible to determine the location of the reactive center.
Role of Molecular Modeling and Computational Chemistry in Identifying Reactive Centers
- Molecular modeling software can calculate the electron density of a molecule.
- Computational chemistry can calculate the energy of a molecule as it undergoes a reaction.
- By identifying the transition state of a reaction, it is possible to determine the location of the reactive center.
Examples of How Reactive Centers Have Been Identified in Specific Molecules
- In the benzene molecule, the reactive center clouds are located on the six carbon atoms.
- In the ethylene molecule, the reactive center clouds are located on the two carbon atoms.
- In the water molecule, the reactive center clouds are located on the oxygen atom.
Placement of Reactive Center Clouds: Identify The Reactive Centers By Placing The Reactive Center Clouds
There are a number of different approaches that can be used to place reactive center clouds on a molecule. One common approach is to use the molecular orbital theory. This theory describes the electrons in a molecule as occupying specific orbitals.
The reactive center clouds can then be placed on the orbitals that are most likely to be involved in a chemical reaction. Another approach is to use the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. This theory describes the electrons in a molecule as being arranged in such a way as to minimize the repulsion between them.
The reactive center clouds can then be placed on the atoms that have the most valence electrons.
Principles Behind Placing Reactive Center Clouds
- Reactive center clouds can be placed using molecular orbital theory.
- Reactive center clouds can be placed using VSEPR theory.
- The goal is to place the reactive center clouds on the atoms that are most likely to be involved in a chemical reaction.
Different Approaches Used for Placing Reactive Center Clouds
- Molecular orbital theory
- VSEPR theory
- Other methods, such as density functional theory (DFT) and quantum chemical calculations
Examples of How Reactive Center Clouds Have Been Placed on Different Molecules
- In the benzene molecule, the reactive center clouds have been placed on the six carbon atoms.
- In the ethylene molecule, the reactive center clouds have been placed on the two carbon atoms.
- In the water molecule, the reactive center cloud has been placed on the oxygen atom.
Applications of Reactive Center Cloud Theory
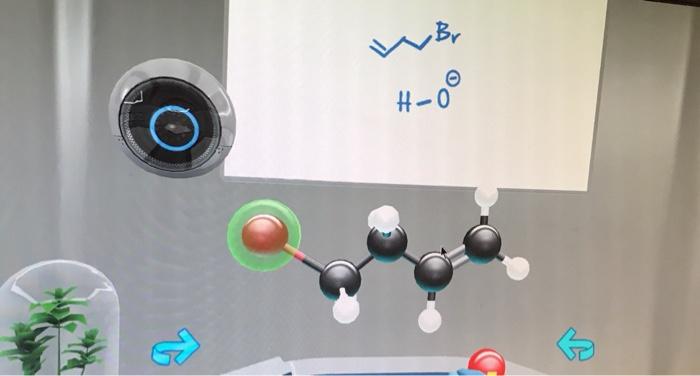
Reactive center cloud theory has a wide range of applications in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. It is used to design new molecules with specific properties, to understand the mechanisms of chemical reactions, and to predict the outcome of chemical reactions.
Applications in Various Fields, Identify the reactive centers by placing the reactive center clouds
- Chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Materials science
Examples of Applications
- Design of new drugs
- Understanding the mechanisms of enzyme catalysis
- Prediction of the outcome of chemical reactions
FAQ Section
What are reactive center clouds?
Reactive center clouds are electron-rich regions within molecules that are responsible for chemical reactivity.
How are reactive centers identified?
Reactive centers can be identified using various methods, including molecular modeling, computational chemistry, and experimental techniques.
What are the applications of reactive center cloud theory?
Reactive center cloud theory has applications in various fields, including drug design, materials science, and environmental chemistry.