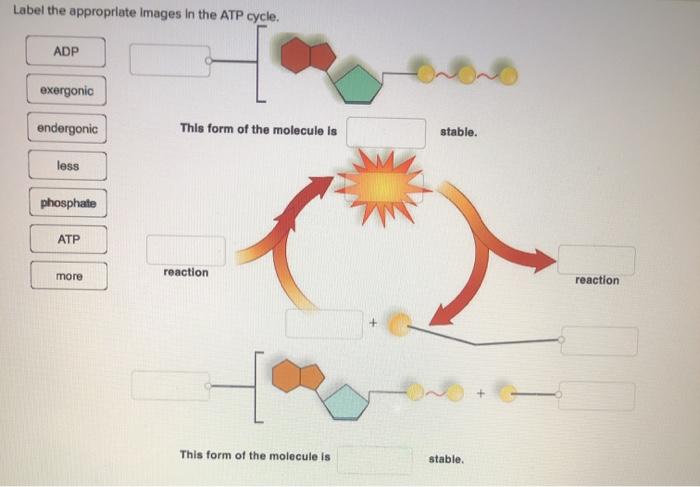
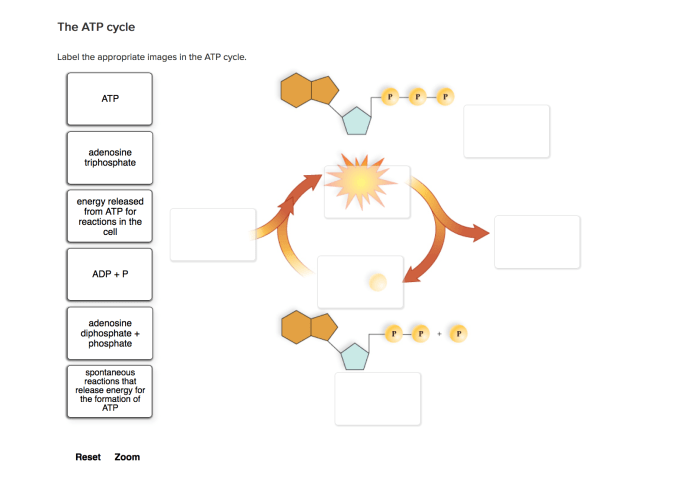
Label the appropriate images in the atp cycle. – Image labeling is a crucial aspect of the ATP cycle, as it provides valuable data for understanding the complex biochemical processes involved. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance, techniques, and best practices associated with image labeling in the ATP cycle, empowering researchers with the knowledge to effectively analyze and interpret visual data.
By understanding the different types of images, labeling challenges, and available techniques, researchers can optimize their image labeling process, ensuring accurate and reliable data for their investigations.
Image Labeling in the ATP Cycle
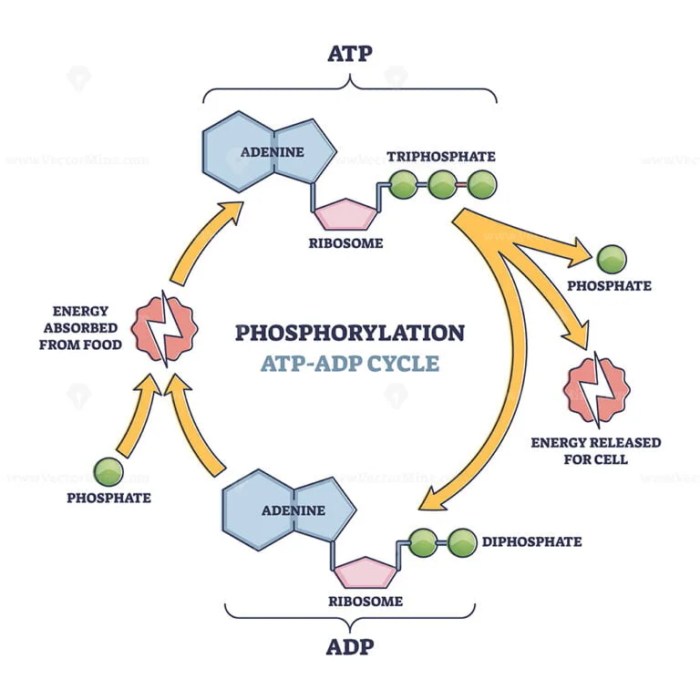
Image labeling is a crucial step in the ATP cycle, as it allows researchers to identify and track the different components of the cycle. This information can then be used to study the dynamics of the cycle and to identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.There
are several different types of images that need to be labeled in the ATP cycle. These include images of the mitochondrial matrix, the inner mitochondrial membrane, and the outer mitochondrial membrane. Each of these images contains different information, and it is important to label them correctly in order to obtain accurate data.There
are a number of challenges associated with image labeling in the ATP cycle. These challenges include the small size of the mitochondria, the complex structure of the mitochondrial membranes, and the presence of artifacts in the images.
Image Labeling Techniques
There are a variety of image labeling techniques that can be used in the ATP cycle. These techniques include manual labeling, semi-automatic labeling, and automatic labeling.Manual labeling is the most accurate method of image labeling, but it is also the most time-consuming.
Semi-automatic labeling is less accurate than manual labeling, but it is faster. Automatic labeling is the fastest method of image labeling, but it is also the least accurate.The choice of image labeling technique depends on the specific needs of the research project.
For projects that require high accuracy, manual labeling is the best option. For projects that require speed, automatic labeling is the best option.
Image Labeling Tools, Label the appropriate images in the atp cycle.
There are a number of different image labeling tools available. These tools include ImageJ, CellProfiler, and Imaris.ImageJ is a free and open-source image labeling tool that is widely used in the scientific community. CellProfiler is a commercial image labeling tool that is designed for high-throughput image analysis.
Imaris is a commercial image labeling tool that is designed for 3D image analysis.The choice of image labeling tool depends on the specific needs of the research project. For projects that require basic image labeling, ImageJ is a good option.
For projects that require more advanced image labeling, CellProfiler or Imaris are better options.
Image Labeling Best Practices
There are a number of best practices that should be followed when labeling images in the ATP cycle. These best practices include:
- Use a consistent labeling scheme.
- Label all images in the same way.
- Use descriptive labels.
- Avoid using abbreviations.
- Check your labels for errors.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your image labels are accurate and consistent. This will make it easier to analyze the data and to identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Questions and Answers: Label The Appropriate Images In The Atp Cycle.
What are the different types of images that need to be labeled in the ATP cycle?
Images typically labeled in the ATP cycle include microscopy images of cells, protein structures, and molecular interactions.
What are the challenges associated with image labeling in the ATP cycle?
Challenges include image complexity, variability, and the need for specialized knowledge to accurately label images.
What are the key best practices for image labeling in the ATP cycle?
Best practices include ensuring accuracy, consistency, and completeness, using appropriate labeling tools, and adhering to established guidelines.